which fissure separates the cerebral hemispheres?
The other hemisphere interprets visual and spatial information. Inferior parietal lobule Wernickes area supramarginal gyrus.
 |
| Chapter 14 The Brain And Cranial Nerves Flashcards Quizlet |
The parieto-occipital sulcus separates the parietal and occipital lobes.
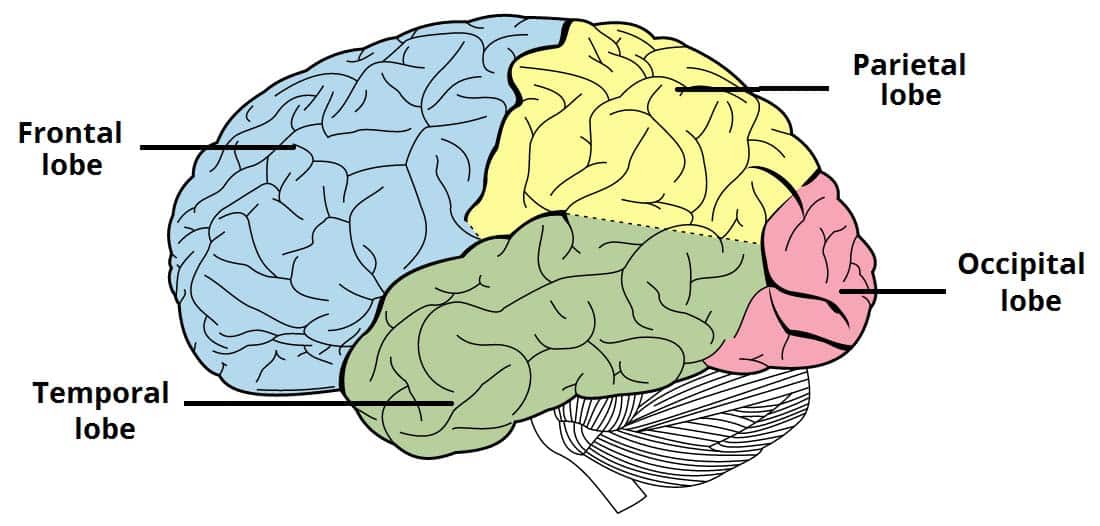
. Cerebrum the largest and uppermost portion of the brain. And the longitudinal fissure divides the two hemispheres. Its superior border is the inferior frontal sulcus which divides it from the middle frontal gyrus its inferior border is the lateral sulcus which divides it from the superior temporal gyrus and its posterior border is. Cerebellar hemispheres seen from front r and back l The Database Center for Life ScienceWikimedia.
The cerebral hemispheres consist of an inner core of. It begins anteriorly from the crista galli of the ethmoid bone and runs in the. Hippocampus - sends memories out to the appropriate part of the cerebral. This crescent-shaped sheet of tissue occupies this fissure and separates the two cerebral hemispheres.
Sulcus shown in. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following is true of the cerebral hemispheres of the human brain. July 22 2022 Reading time. Genu of the corpus callosum inferior view The genu Latin for knee of the corpus callosum is observed in the center of the section medial to the frontal lobes and the frontal anterior horns of the.
The two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex are part of the forebrain Figure 317 which is the largest part of the brain. The median longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres connected by the corpus callosumAlthough the macrostructure of the two hemispheres appears to be almost identical. 11 minutes The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain spanning all three cranial fossae. Each of these hemispheres has an outer layer of grey matter the cerebral cortex that is supported by an inner layer of white matterIn eutherian placental.
The vermis Latin for worm separates the cerebellums hemispheres. In neuroanatomy the central sulcus also central fissure fissure of Rolando or Rolandic fissure after Luigi Rolando is a sulcus or groove in the cerebral cortex in the brains of vertebratesIt is sometimes confused with the longitudinal fissure. The surface of the brain known as the cerebral cortex is very uneven characterized by a distinctive pattern of folds or bumps known as gyri singular. 3 Nearly the entire surface of the.
Lorenzo Crumbie MBBS BSc Reviewer. Interhemispheric Medial Longitudinal Fissure. These gyri and sulci form important landmarks that allow us to separate the brain into functional. It lies largely in the anterior cranial fossa of the skull leaning on the orbital plate of the frontal bone.
The STS is located under the lateral fissure which is the. This is a deep furrow located down the center of the brain that separates the left and right brain hemispheres. At its inferior end the sulcus is continuous with the anterior part of the calcarine sulcus. Twelve pairs of nerves that originate in the brain exit the skull and lead to the head neck and torso.
1 The longitudinal fissure separates the cerebral hemispheres from the cerebellum. Medially it is confined by the medial longitudinal fissure which divides both cerebral hemispheres. The lateralization of brain function is the tendency for some neural functions or cognitive processes to be specialized to one side of the brain or the other. Those who have a checking or savings account but also use financial alternatives like check cashing services are considered underbanked.
The prominent parietoocccipital sulcus separates the occipital from the parietal lobe. This deep grove separates the parietal and temporal lobes. At the base of this fissure lies a thick bundle of nerve fibres called the corpus callosum which provides a communication link between the hemispheres. These gyri and sulci form important landmarks that allow us to separate the brain into functional centers.
The lateral sulcus sylvian fissure is the most lateral boundary separating it from the temporal lobe. The frontal lobe is the largest lobe of the brain comprising almost one-third of the hemispheric surface. Topography of the cerebral hemispheres Author. The central sulcus is a prominent landmark of the brain separating the parietal lobe from the frontal lobe and the.
Dimitrios Mytilinaios MD PhD Last reviewed. Thick band of fibers that connects the left and right brain hemispheres. The cerebral hemispheres are separated by a deep groove the longitudinal cerebral fissure. The longitudinal fissure or cerebral fissure great longitudinal fissure median longitudinal fissure interhemispheric fissure is the deep groove that separates the two cerebral hemispheres of the vertebrate brainLying within it is a continuation of the dura mater one of the meninges called the falx cerebri.
The vertebrate cerebrum is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove the longitudinal fissureThe brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Fissure of Sylvius Lateral Sulcus. It is a funnel-like structure that extends from the decussation of the great pyramids passes through the foramen magnum which is the largest of all the foramina and fissures of the skull to the inferior pontine sulcus pontomedullary grooveAs the medulla continues upward. Sulcus shown in Figure 1.
The superior temporal sulcus STS is the sulcus separating the superior temporal gyrus from the middle temporal gyrus in the temporal lobe of the brainA sulcus plural sulci is a deep groove that curves into the largest part of the brain the cerebrum and a gyrus plural gyri is a ridge that curves outward of the cerebrum. 2 Nearly the entire surface of the cerebral hemispheres is marked by shallow grooves called gyri. The parietal lobe is defined by three anatomical boundaries. The frontal lobe forms the most anterior portion of the cerebral hemisphere and is separated from the parietal lobe posteriorly by the central sulcus and from.
The longitudinal fissure along with the falx cerebri that runs within the fissure divides the cerebrum into left and right hemispheres. The composite parts can be classified based on their embryological origin functional roles or their topography. The Database Center for Life ScienceWikimedia Commons. On the opposite end it extends slightly onto the superolateral surface of each cerebral hemisphere.
The cerebrum controls somatosensory motor language cognitive thought memory emotions hearing and vision. Gyrus and grooves known as sulci singular. The left hemisphere controls the right half of the body and vice versa because of a crossing of. The brain consists of the cerebrum cerebellum and brainstem.
Gyrus and grooves known as sulci singular. The falx cerebri is the largest of the four partitions of the dura mater and represents an invagination of the meningeal layer of dura into the longitudinal fissure of the brain. The deep groove separating the hemispheres is called the longitudinal fissure or cerebral fissure. The medulla oblongata or medulla is the narrowest and most caudal part of the brainstem.
The central sulcus separates the parietal lobe from the frontal lobe. Taking up the majority of the brain space is the cerebrum. Postcentral gyrus primary sensory area superior parietal lobule. The forebrain contains the.
The left hemisphere and the right hemisphere. The corpus callosum a wide ribbon of nerves is located within this fissure. Fissure of Sylvius Lateral Sulcus Deep grove that separates the parietal. The most prominent sulcus known as the longitudinal fissure is the deep groove that separates the brain into two halves or hemispheres.
The surface of the brain known as the cerebral cortex is very uneven characterized by a distinctive pattern of folds or bumps known as gyri singular. It traverses the medial surface at an almost vertical trajectory. The underbanked represented 14 of US. One hemisphere usually the left is functionally dominant controlling language and speech.
The two hemispheres remain in. The inferior frontal gyrus IFG gyrus frontalis inferior is the lowest positioned gyrus of the frontal gyri of the frontal lobe and is part of the prefrontal cortex. The inner surfaces of the two hemispheres are convoluted. The cerebrum consists of the cerebral hemispheres and accounts for two-thirds of the total weight of the brain.
The cerebrum is divided into the left and right hemispheres by a deep longitudinal fissure.
 |
| Sylvian Fissure Definition |
 |
| Lateral Medial And Inferior Surfaces Of The Cerebral Hemispheres Neuroanatomy The Neurosurgical Atlas |
 |
| Cerebral Hemisphere Wikiwand |
 |
| 11 1 The Cerebrum Biology Libretexts |
 |
| Neuroanatomy Online Lab 1 Overview Of The Nervous System Telencephalon Fissures Lobes And Sulci |
Posting Komentar untuk "which fissure separates the cerebral hemispheres?"